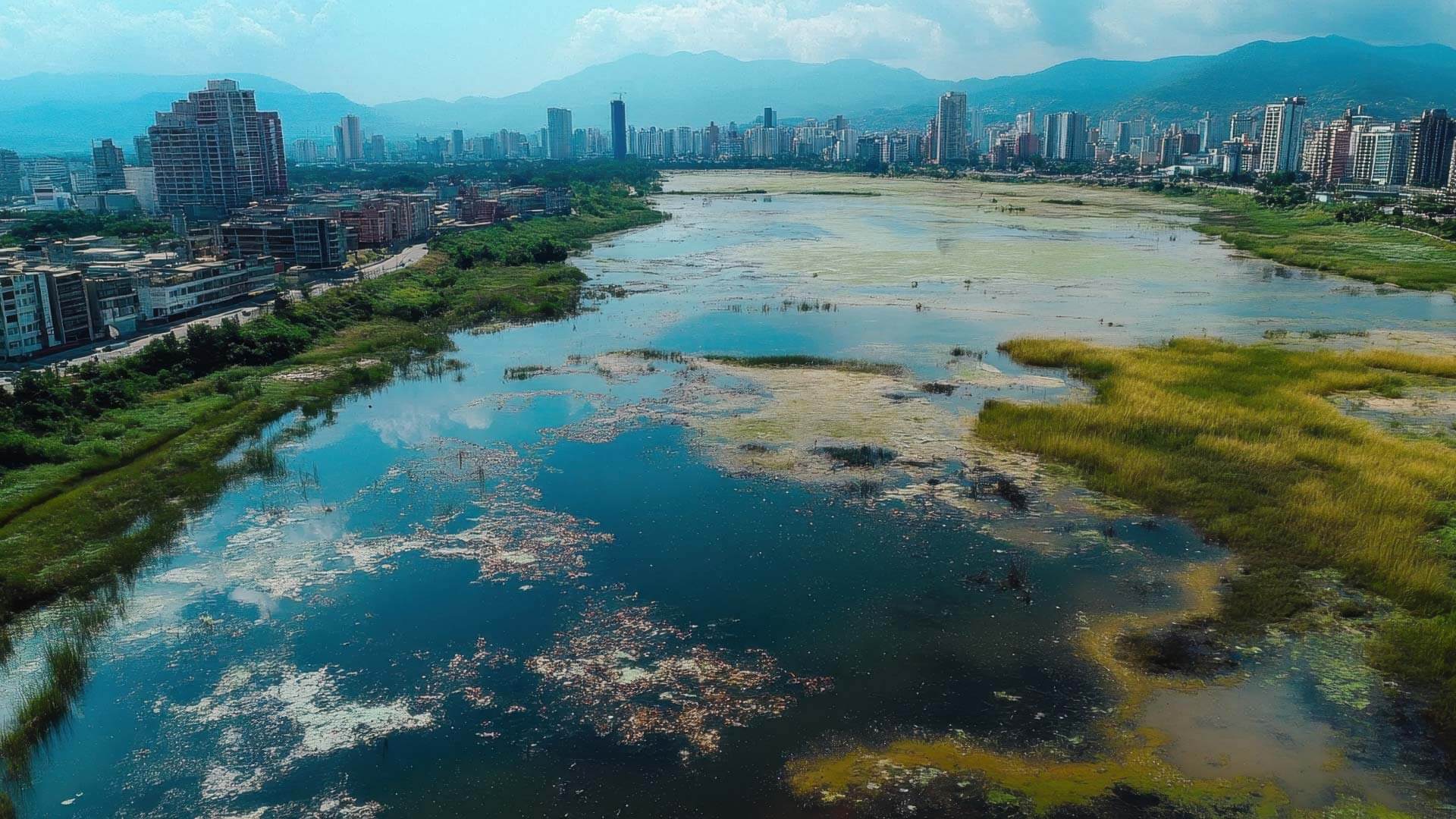
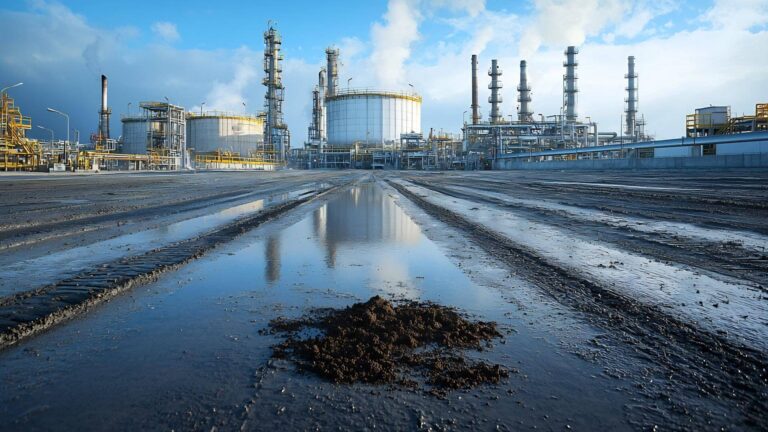
As industrial activities, urban expansion, and agricultural practices continue to impact the environment, the need for environmental remediation has never been greater. Contaminated soil, groundwater, and air pose significant risks to human health and ecosystems, requiring effective solutions to mitigate pollution and restore environmental balance. Environmental remediation services play a critical role in identifying, managing, and eliminating pollutants from affected areas, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and promoting long-term sustainability.
Over the years, environmental remediation companies have adopted a range of methods to address contamination, from traditional excavation and chemical treatments to more advanced biotechnological and nanotechnological solutions. As pollution challenges grow more complex, there is an increasing demand for innovative and cost-effective approaches that minimize environmental impact while maximizing efficiency. Emerging technologies such as bioremediation, phytoremediation, and nanotechnology are revolutionizing the way contaminants are removed or neutralized, paving the way for a more sustainable future in pollution management. By leveraging cutting-edge advancements, environmental remediation continues to evolve, offering new opportunities to combat contamination in a more effective and eco-friendly manner.
Understanding Environmental Remediation

What Is Environmental Remediation?
Environmental remediation refers to the process of removing or neutralizing pollutants from soil, water, and air to restore environmental health and ensure compliance with safety regulations. This essential practice is designed to mitigate the adverse effects of industrial waste, chemical spills, heavy metals, and other hazardous contaminants that threaten ecosystems and human well-being. By employing various physical, chemical, and biological methods, environmental remediation services help reverse environmental damage and prevent further pollution.
Common Contaminants in Soil, Water, and Air
Pollutants that require environmental remediation come from various sources, including industrial processes, agricultural runoff, and improper waste disposal. Some of the most common contaminants include:
- Soil Contaminants: Heavy metals (lead, mercury, arsenic), petroleum hydrocarbons, pesticides, and industrial solvents
- Water Contaminants: Oil spills, chlorinated solvents, nitrates, pharmaceutical waste, and microplastics
- Air Contaminants: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, and greenhouse gases
These pollutants can lead to soil degradation, water scarcity, and air quality issues that impact public health and biodiversity. Effective environmental remediation services focus on identifying and targeting these contaminants to ensure a cleaner, healthier environment.
The Role of Environmental Remediation Companies in Pollution Management

As pollution challenges become more complex, environmental remediation companies play a vital role in implementing solutions that effectively remove or neutralize contaminants. These companies specialize in site assessments, contamination analysis, and the application of advanced remediation technologies to restore affected areas. Their expertise ensures that remediation efforts comply with environmental regulations, minimize ecological disruption, and promote sustainable land and water use.
Environmental remediation continues to evolve, with advancements in remediation techniques offering more efficient and eco-friendly methods to tackle pollution. Whether addressing industrial waste sites, restoring contaminated groundwater, or improving air quality, environmental remediation services are essential for maintaining environmental integrity and protecting future generations from the harmful effects of pollution.
Traditional Environmental Remediation Methods
While technological advancements continue to reshape pollution management, traditional environmental remediation methods remain widely used for addressing soil, water, and air contamination. These time-tested approaches include physical and chemical remediation techniques, groundwater treatment systems, and containment strategies. Environmental remediation services rely on these methods to remove, neutralize, or isolate hazardous substances, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and preventing further ecological damage.
Physical and Chemical Remediation
One of the most common strategies in environmental remediation is the use of physical and chemical treatments to extract or neutralize contaminants. These methods include:
- Excavation and Removal: Contaminated soil is physically dug out and transported to a designated disposal or treatment site. This is one of the fastest ways to eliminate pollutants, but can be costly and disruptive to the surrounding environment.
- Soil Washing: A process that uses water, chemical solutions, or biological agents to extract contaminants from soil, leaving behind cleaner material that can be safely reused or returned to the environment.
- Chemical Treatments: The introduction of chemical agents to break down or immobilize hazardous substances. Oxidation, reduction, and stabilization techniques are commonly used to render pollutants less harmful or easier to remove.
Pump-and-Treat Systems for Groundwater Purification
Groundwater contamination is a major concern that requires specialized environmental remediation services to restore water quality. Pump-and-treat is one of the most widely used methods for addressing groundwater pollution:
- Extraction of Contaminated Water: Polluted groundwater is pumped to the surface and processed through filtration or chemical treatment systems to remove toxins, heavy metals, and industrial pollutants.
- Treatment and Reintroduction: Once purified, the treated water is either discharged back into the environment or safely reused. This method is effective for addressing long-term contamination but can be resource-intensive and require years of operation.
Containment Strategies: Isolating Contaminants
In cases where removal is not feasible, environmental remediation companies often use containment strategies to prevent contaminants from spreading:
- Landfill Containment: Contaminated materials are securely deposited in lined landfills designed to prevent leaching into soil and water sources.
- Capping Systems: To prevent exposure and infiltration, a physical barrier, such as clay or synthetic liners, is placed over contaminated soil or waste sites.
- Barrier Walls and Permeable Reactive Barriers (PRBs): Structures designed to block or filter contaminants in groundwater, allowing clean water to pass while trapping pollutants.
Traditional environmental remediation methods remain essential in managing pollution and protecting ecosystems from harmful substances. By employing physical removal, chemical treatments, and strategic containment, environmental remediation services help mitigate the risks posed by hazardous waste, ensuring safer environments for humans and wildlife.
Bioremediation: Harnessing Microorganisms for Pollution Cleanup
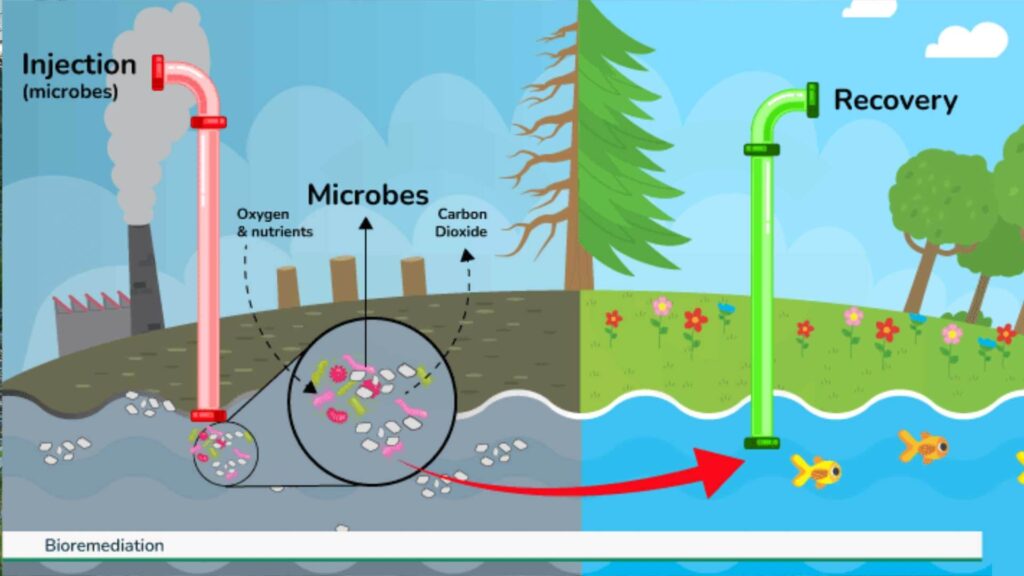
Bioremediation is an innovative and eco-friendly environmental remediation technique that utilizes the natural abilities of microorganisms, fungi, and plants to break down pollutants in contaminated environments. Environmental remediation services are increasingly adopting this method due to its cost-effectiveness and minimal ecological disruption. By utilizing biological processes, bioremediation transforms hazardous substances into harmless byproducts, making it an effective solution for soil, water, and air pollution.
How Bioremediation Works
Bioremediation relies on the metabolic activities of bacteria, fungi, and certain plants to degrade or neutralize contaminants. These organisms consume pollutants as a source of energy or convert them into less harmful compounds through enzymatic reactions. Key mechanisms include:
- Bacterial Degradation: Specialized bacteria break down hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and industrial chemicals into non-toxic substances.
- Fungal Remediation: Mycoremediation, or fungal-based remediation, uses fungi to absorb and break down persistent organic pollutants.
- Phytoremediation: Certain plants, known as hyperaccumulators, absorb and store contaminants in their tissues, preventing further spread in the environment.
By leveraging these biological processes, environmental remediation companies can address contamination without relying on harsh chemical treatments or invasive removal methods.
Types of Bioremediation: In-Situ vs. Ex-Situ Approaches
Bioremediation can be categorized into two main approaches based on how and where the treatment occurs:
- In-Situ Bioremediation: Contaminants are treated directly at the site without excavation. This approach includes techniques such as bioaugmentation (introducing beneficial microorganisms) and venting (stimulating microbial activity with oxygen and nutrients). It is a low-cost, minimally invasive method commonly used for groundwater and soil remediation.
- Ex-situ bioremediation involves removing and treating contaminated materials in a controlled environment. Methods such as biopiles (which degrade pollutants like compost) and bioreactors (engineered systems that optimize microbial activity) allow for faster remediation but require more resources and infrastructure.
Both methods are widely used by environmental remediation services, with the choice depending on factors such as contamination type, site conditions, and regulatory requirements.
Advantages and Challenges of Bioremediation
Bioremediation offers several advantages that make it an attractive option for environmental remediation companies:
- Eco-Friendly and Sustainable: Utilizes natural organisms to degrade pollutants without introducing harmful chemicals.
- Cost-Effective: Often requires lower investment compared to excavation and chemical treatments.
- Minimal Site Disruption: In-situ methods allow remediation without extensive excavation or land disturbance.
However, bioremediation also comes with challenges:
- Time-Intensive: Biological processes can take weeks or months to break down contaminants fully.
- Limited to Specific Pollutants: Not all contaminants can be effectively treated with bioremediation, particularly heavy metals and certain synthetic compounds.
- Requires Optimal Conditions: For microbial activity to be effective, factors such as temperature, oxygen levels, and pH must be carefully managed.
Despite these challenges, bioremediation remains a promising and sustainable environmental remediation approach, helping to restore contaminated sites while preserving ecological integrity. By integrating bioremediation into their strategies, environmental remediation companies can offer innovative and environmentally responsible solutions for pollution cleanup.
Phytoremediation: Using Plants for Contaminant Absorption

Phytoremediation is an innovative environmental remediation technique that uses plants to absorb, stabilize, or filter contaminants from soil and water. This natural approach is gaining popularity among environmental remediation services due to its cost-effectiveness, sustainability, and minimal ecological disturbance. By using specialized plant species, phytoremediation helps remove heavy metals, organic pollutants, and excess nutrients from contaminated sites, making it a viable solution for improving environmental health.
Mechanisms of Phytoremediation
Different plants use various mechanisms to remediate contamination, depending on the type of pollutant and environmental conditions. The three primary phytoremediation processes include:
- Phytoextraction: Plants absorb contaminants—such as heavy metals—through their roots and store them in their stems, leaves, or other tissues. Once mature, these plants can be harvested and safely disposed of, effectively removing pollutants from the environment.
- Phytostabilization: Instead of absorbing contaminants, plants immobilize pollutants in the soil by reducing their mobility and bioavailability. This prevents further contamination of groundwater and surrounding ecosystems.
- Rhizofiltration: The root systems of certain plants absorb or filter out contaminants from water, making it a valuable technique for treating polluted lakes, rivers, and groundwater.
These natural processes allow environmental remediation companies to address contamination with minimal disruption to the land, promoting long-term sustainability in pollution management.
Best Plant Species for Remediation
Certain plants, known as hyperaccumulators, are particularly effective in absorbing and storing pollutants. These species are commonly used in environmental remediation services due to their ability to thrive in contaminated environments and accumulate high levels of toxic substances. Some of the best plants for phytoremediation include:
- Sunflowers (Helianthus annuus) – Effective in removing lead, arsenic, and radioactive contaminants from soil and water.
- Indian Mustard (Brassica juncea) – Known for absorbing heavy metals such as cadmium, nickel, and lead.
- Poplar and Willow Trees – Used for phytostabilization and hemofiltration to clean up petroleum hydrocarbons and organic contaminants.
- Alpine Pennycress (Thlaspi caerulescens) – Highly efficient at absorbing zinc and cadmium from contaminated soils.
By strategically planting these species, environmental remediation companies can naturally extract or contain harmful pollutants without relying on expensive or invasive remediation techniques.
Applications and Effectiveness
Phytoremediation has been successfully applied to various contamination scenarios, including:
- Soil Remediation: Restoring farmland, industrial sites, and mining-affected areas by removing heavy metals and toxic compounds.
- Water Treatment: Using aquatic plants for hemofiltration to clean up contaminated lakes, wetlands, and groundwater sources.
- Erosion and Runoff Control: Preventing contaminants from spreading by stabilizing soil in polluted areas.
While phytoremediation is slower than some conventional environmental remediation methods, it offers a sustainable and cost-effective alternative for long-term site restoration. By integrating phytoremediation into their strategies, environmental remediation services can help restore polluted environments naturally while promoting biodiversity and ecological resilience.
Advanced Chemical and Electrochemical Remediation Techniques
As contamination challenges become more complex, environmental remediation continues to evolve with advanced chemical and electrochemical methods designed to accelerate pollutant breakdown and removal. These high-efficiency techniques are widely adopted by environmental remediation services for treating contaminated soil and groundwater, particularly in areas where traditional methods may be ineffective. By utilizing reactive agents, electric fields, and catalytic processes, these approaches provide targeted, scalable solutions for pollution management.
Chemical Oxidation and Reduction: Breaking Down Contaminants with Reactive Agents
Chemical oxidation and reduction (redox) processes are widely used in environmental remediation to break down hazardous substances into less harmful or inert compounds. These methods involve the injection of reactive agents to alter contaminants at a molecular level chemically:
- Chemical Oxidation: Oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide, ozone, or potassium permanganate are introduced to degrade organic pollutants, petroleum hydrocarbons, and chlorinated solvents in soil and water. This method accelerates natural decomposition and prevents toxic buildup.
- Chemical Reduction: Reducing agents like zero-valent iron (ZVI) or sodium dithionite convert contaminants into less toxic or immobile forms. This technique is particularly effective for treating heavy metals, nitrates, and halogenated compounds.
By integrating these chemical processes, environmental remediation companies can rapidly treat contaminated sites, minimizing long-term environmental risks and improving soil and water quality.
Electrokinetic Remediation: Using Electric Fields to Mobilize and Remove Pollutants
Electrokinetic remediation is an innovative approach that applies low-voltage electrical fields to contaminated soil and groundwater, mobilizing pollutants for easier extraction. This method is particularly effective for fine-grained soils with low permeability, where traditional remediation techniques struggle to reach embedded contaminants.
Key mechanisms of electrokinetic remediation include:
- Electromigration: Charged contaminants, such as heavy metals, move toward oppositely charged electrodes, where they can be collected and removed.
- Electroosmosis: Water movement through soil pores enhances contaminant mobility, allowing for easier flushing and extraction.
- Electrophoresis: Charged particles, including organic pollutants, migrate through the soil under an applied electric field, increasing the efficiency of environmental remediation services in pollutant removal.
This technique is often used in combination with other remediation strategies, enabling environmental remediation companies to treat contaminated sites with greater precision and efficiency.
Catalytic Processes: Accelerating Remediation with Advanced Catalysts
Catalytic remediation leverages advanced catalyst materials to enhance chemical reactions that break down pollutants more efficiently. These processes are particularly useful for degrading persistent organic pollutants (POPs), industrial solvents, and petroleum-based contaminants.
Some key catalytic techniques include:
- Photocatalysis: Using light-activated catalysts, such as titanium dioxide (TiO₂), to degrade pollutants in soil and water through oxidation.
- Enzymatic Catalysis: Employing biological catalysts (enzymes) to accelerate the breakdown of hydrocarbons, pesticides, and industrial chemicals.
- Nanocatalysis: Utilizing nanomaterials to improve reaction rates and increase the efficiency of contaminant removal, a rapidly growing area in environmental remediation.
By integrating catalytic processes into environmental remediation services, companies can achieve faster, more effective contaminant breakdown with minimal secondary waste production.
Advanced chemical and electrochemical remediation techniques offer powerful solutions for pollution management. They allow environmental remediation companies to treat contaminated environments with precision, speed, and environmental responsibility. These methods continue to drive innovation in the industry, ensuring the safe restoration of ecosystems affected by industrial and chemical pollutants.
Nanotechnology in Environmental Remediation
Nanotechnology is revolutionizing environmental remediation by providing highly efficient, scalable, and cost-effective solutions for pollution removal. Due to their extremely small size and high reactivity, nanomaterials offer unique advantages in targeting and neutralizing contaminants that traditional remediation methods struggle to address. As environmental remediation services continue to evolve, the use of nanoparticles is gaining traction for its ability to accelerate pollutant degradation, enhance contaminant absorption, and improve overall remediation efficiency.
Role of Nanoparticles in Pollution Removal
Nanoparticles are engineered to interact at the molecular level with contaminants, breaking them down or transforming them into less harmful substances. These ultra-small particles possess a high surface area-to-volume ratio, which increases their reactivity and effectiveness in remediation applications. Some key ways nanoparticles aid in environmental remediation include:
- Adsorption and Binding: Nanoparticles can effectively trap pollutants, such as heavy metals and organic chemicals, preventing them from spreading further in soil or water.
- Catalytic Degradation: Many nanomaterials act as catalysts, accelerating chemical reactions that break down toxic pollutants into non-harmful byproducts.
- Oxidation and Reduction Processes: Some nanoparticles facilitate redox reactions that neutralize hazardous substances, such as hydrocarbons and chlorinated solvents, enhancing remediation effectiveness.
With their ability to target contaminants at the microscopic level, nanotechnology is transforming how environmental remediation companies address pollution in diverse settings, including industrial sites, water treatment facilities, and air purification systems.
Types of Nanomaterials Used in Environmental Remediation
Different types of nanomaterials are utilized in environmental remediation services, each offering unique properties for specific contamination challenges:
- Carbon-Based Nanomaterials: Activated carbon nanotubes and graphene-based materials excel at absorbing heavy metals and organic pollutants from water and soil.
- Metal-Based Nanoparticles: Zero-valent iron (nZVI) is widely used for breaking down chlorinated solvents, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. Silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles are also effective in antimicrobial and photocatalytic remediation processes.
- Polymeric Nanoparticles: These engineered materials are designed to encapsulate and remove specific contaminants, providing controlled-release solutions for gradual pollutant breakdown.
By incorporating these advanced nanomaterials, environmental remediation companies can enhance the efficiency and precision of pollution cleanup while reducing the need for large-scale excavation or chemical treatments.
Potential Risks and Future Applications
Despite the promising benefits of nanotechnology in environmental remediation, there are concerns regarding its long-term environmental and health impacts. Some of the key risks include:
- Toxicity and Bioaccumulation: Certain nanoparticles may persist in the environment, potentially accumulating in ecosystems and affecting aquatic life.
- Regulatory Challenges: The use of nanotechnology in environmental remediation services is still evolving, and safety regulations continue to be developed.
- Unknown Long-Term Effects: More research is needed to fully understand how nanoparticles behave in different environmental conditions and their potential unintended consequences.
Looking ahead, nanotechnology is expected to play an even greater role in environmental remediation, with advancements in biodegradable nanomaterials, smart nanosensors for real-time pollution detection, and AI-driven optimization of nanoparticle applications. As environmental remediation companies continue to explore these technologies, the industry is moving toward more precise, sustainable, and highly effective solutions for tackling pollution at its source.
The Role of Environmental Remediation Companies in Innovation
As pollution challenges become more complex, environmental remediation companies are at the forefront of driving innovation to develop more efficient and sustainable solutions. By investing in advanced technologies, adapting to evolving regulations, and integrating data-driven approaches, these industry leaders are reshaping the landscape of environmental remediation services. The push for cutting-edge methods is not only improving pollutant removal efficiency but also reducing costs and minimizing environmental disruption.
How Industry Leaders Are Driving Change
Leading environmental remediation companies are continually exploring new technologies to enhance their ability to clean up contaminated sites more effectively. Some of the key advancements include:
- Bioremediation and Phytoremediation: Utilizing microorganisms and plants to break down pollutants in soil and water naturally.
- Nanotechnology in Pollution Control: Leveraging nanoparticles to remove heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and industrial contaminants with greater precision.
- Electrochemical and Catalytic Processes: Accelerating chemical reactions to neutralize pollutants more efficiently and with lower energy consumption.
By integrating these innovations, environmental remediation services are becoming more sustainable and scalable. They allow for the cleanup of a wider range of contaminants while reducing reliance on costly excavation or chemical treatments.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
As environmental policies continue to evolve, environmental remediation companies must adapt their strategies to meet new regulations and industry standards. Compliance with federal, state, and international environmental laws is essential for ensuring that remediation efforts align with sustainability goals and public health protections. Key regulatory considerations include:
- Contaminant Thresholds: Adhering to government-mandated limits on pollutants in soil, water, and air.
- Waste Disposal and Management: Ensuring that removed contaminants are safely processed and disposed of without causing secondary environmental harm.
- Eco-Friendly Approaches: Meeting stricter regulations that encourage greener remediation practices, such as low-impact dredging, chemical-free treatments, and renewable energy-powered cleanup systems.
By anticipating regulatory shifts, environmental remediation services can operate more efficiently while maintaining compliance with environmental protection agencies and sustainability initiatives.
Future Trends in Environmental Remediation Services
The future of environmental remediation is being shaped by emerging technologies that improve precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Some of the most significant trends include:
- AI and Machine Learning: Advanced algorithms are being used to analyze contamination patterns, predict remediation outcomes, and optimize treatment strategies.
- Automation and Robotics: Remotely operated systems and drones are being deployed for site assessments, contamination mapping, and automated pollutant removal.
- Real-Time Data Monitoring: The integration of smart sensors and IoT technology is enabling continuous environmental monitoring, ensuring that remediation efforts are adjusted in real-time for maximum effectiveness.
As these advancements continue to evolve, environmental remediation companies will play a crucial role in implementing and refining these next-generation solutions. By leveraging technology, staying compliant with regulations, and prioritizing sustainability, the industry is paving the way for more effective and environmentally responsible remediation services.
Conclusion
Innovation in environmental remediation is transforming the way pollution is managed, making cleanup efforts more efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective. From traditional methods like excavation and chemical treatments to advanced approaches such as bioremediation, nanotechnology, and electrochemical remediation, environmental remediation services continue to evolve to meet the challenges of complex contamination. These advancements not only enhance pollutant removal but also minimize environmental disruption, ensuring that soil, water, and air quality can be restored with long-term sustainability in mind. As pollution threats grow due to industrial activities and climate change, the demand for innovative remediation strategies will only continue to rise.
Environmental remediation companies are at the forefront of this transformation, driving change through investment in new technologies, regulatory compliance, and data-driven solutions. By incorporating artificial intelligence, automation, and real-time monitoring, the industry is becoming more proactive in tackling contamination before it escalates. As these cutting-edge techniques become more widely adopted, the future of environmental remediation looks promising, with cleaner ecosystems, safer communities, and a more sustainable approach to pollution management.




