Proper maintenance of your dredge pump is essential for ensuring consistent performance and extending its lifespan. Dredge pumps play a crucial role in efficiently moving slurry, sediment, and debris in dredging operations. Well-maintained pumps operate more efficiently, reduce downtime, and minimize repair costs, ultimately improving project productivity and profitability. Extending the lifespan of a dredge pump lowers energy consumption, enhances output consistency, and prevents costly failures that can lead to delays and increased expenses. For demanding projects like mining, construction, or environmental cleanup, a reliable dredge pump can significantly impact operational success.
Different dredge pumps have unique maintenance needs. A gold dredge pump handles abrasive materials and fine sediments, requiring frequent impeller inspections and the use of wear-resistant materials. A suction dredge pump relies on strong vacuum pressure, making regular suction line inspections and proper priming essential for maintaining efficiency. Understanding these specific maintenance requirements and following a structured plan helps prevent issues and extend the life of your dredge pump.
Understanding Your Dredge Pump
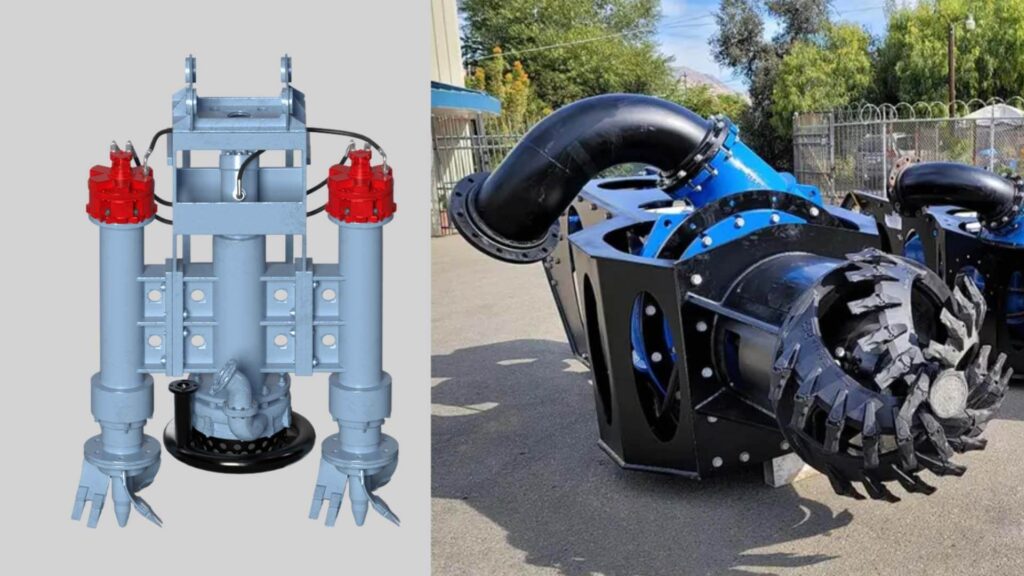
Types of Dredge Pumps
Dredge pumps are specialized equipment designed to move high volumes of water, slurry, and sediment during dredging operations. The type of dredge pump you use will depend on the nature of your project, the material being dredged, and the working environment. Here’s an overview of the most common types of dredge pumps:
- Hydraulic Dredge Pumps – These pumps are powered by hydraulic systems and are known for their high power and efficiency. They are ideal for heavy-duty dredging applications where consistent performance under extreme conditions is required. Hydraulic dredge pumps are often used in mining, construction, and large-scale environmental projects.
- Electric Dredge Pumps – Electric dredge pumps are powered by electric motors, making them suitable for environments where electrical infrastructure is available. They are generally quieter than hydraulic pumps and offer precise control over flow rates and pressure. Electric dredge pumps are commonly used for industrial and environmental cleanup projects.
- Submersible Dredge Pumps – These pumps are designed to operate underwater, directly at the dredging site. Their ability to work at the source of sediment makes them highly effective for handling high concentrations of solids. Submersible dredge pumps are commonly used in river and lake dredging, mining, and marine construction.
Gold dredge pumps and suction dredge pumps are designed for more specialized applications:
- Gold Dredge Pumps – Gold dredge pumps are built to handle the fine, abrasive materials encountered in gold mining operations. Their design often includes reinforced impellers and wear-resistant materials to withstand constant exposure to sediment and heavy particles.
- Suction Dredge Pumps – Suction dredge pumps rely on strong vacuum pressure to lift sediment from the waterbed and transport it through the pump system. Maintaining suction efficiency requires regular inspection of suction lines and impeller integrity to prevent clogging and loss of pressure.
Key Components of a Dredge Pump
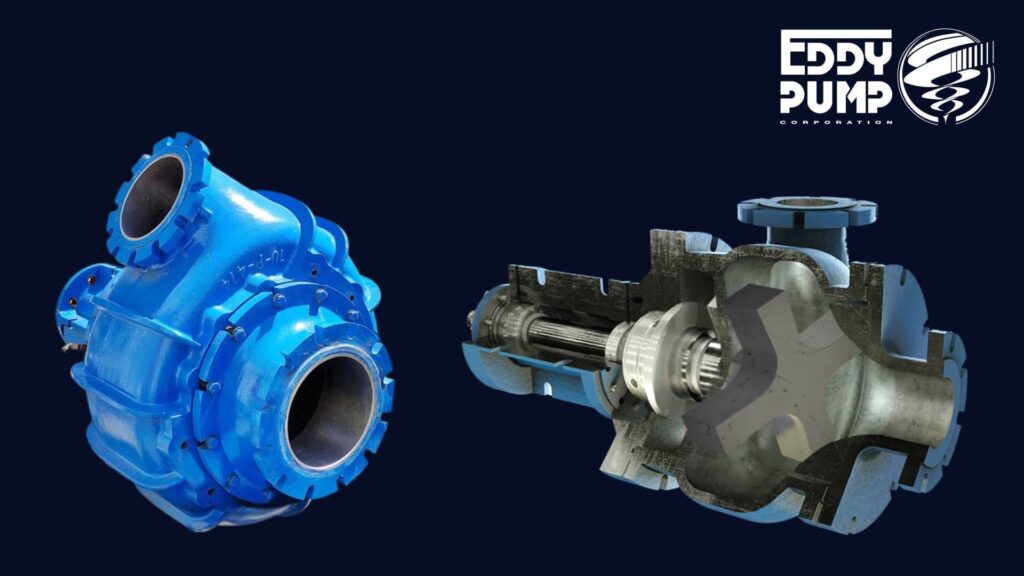

Understanding the core components of a dredge pump is essential for proper maintenance and efficient operation. Each part plays a vital role in ensuring the pump functions effectively under challenging dredging conditions:
- Impellers – The impeller is the heart of the dredge pump. It generates the force that moves the slurry or sediment through the pump. Impellers are typically made from hardened materials to withstand abrasive wear. Regular inspection for wear and damage is essential for maintaining peak performance.
- Casings —he casing houses the impeller and directs the flow of material through the pump. CIt isdesigned to withstand high pressure and abrasion. Damaged or worn casings can reduce pump efficiency and lead to leaks or failures.
- Seals and Bearings —eals and bearings ensure smooth operation by minimizing friction and preventing leakage. Proper lubrication and regular inspection oelp avoid overheating and mechanical failure.
- Suction and Discharge Lines – The suction line draws sediment and water into the pump, while the discharge line expels the mixture. Keeping these lines clear of blockages and ensuring they are properly sealed is critical for maintaining consistent flow and pressure.
Understanding how these components work together allows operators to identify and address issues before they lead to costly downtime. Whether you’re operating a gold dredge pump or a suction dredge pump, regular inspection and maintenance of these key components will significantly improve performance and extend the lifespan of your dredge pump.
Daily and Routine Maintenance Best Practices

Regular maintenance is key to keeping your dredge pump operating at peak efficiency and preventing costly breakdowns. Establishing a consistent daily and routine maintenance schedule helps identify minor issues before they escalate into major problems, extending the lifespan of your dredge pump and improving overall performance.
Pre-Operation Inspection
Conducting a thorough inspection before starting your dredge pump ensures that it is in proper working condition and ready for operation. Skipping this step can lead to reduced efficiency and potential damage during use.
- Check for Visible Damage or Wear on Impellers and Casings – The impeller is the primary working component of a dredge pump, responsible for generating the suction and discharge pressure. Look for signs of wear, cracks, or damage on the impeller and casing. Worn-out components reduce efficiency and increase the risk of failure.
- Ensure Proper Alignment of the Pump and Motor – Misalignment between the pump and motor can cause vibration, excessive wear on bearings, and reduced efficiency. Use a laser alignment tool or alignment gauge to verify proper positioning.
- Verify that All Seals and Fittings Are Secure – Loose or damaged seals can lead to leaks and pressure loss, reducing the pump’s suction and discharge capacity. Tighten all bolts and fittings, and replace any worn seals before operation.
Pre-operation checks should also focus on the material being handled for specialized equipment such as a gold dredge pump or a suction dredge pump. Gold dredge pumps encounter highly abrasive material, requiring extra attention to impeller wear and casing integrity. Suction dredge pumps rely heavily on vacuum pressure, so ensuring the suction line is clear and airtight is critical for maintaining strong suction.
Lubrication and Greasing
Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction and preventing premature wear of moving components within a dredge pump. Without adequate lubrication, seals and bearings can overheat and fail, leading to costly repairs and downtime.
- The importance of Using Manufacturer-Recommended Lubricants—Always use lubricants and grease specified by the pump manufacturer. Using the wrong type of lubricant can cause chemical reactions that degrade seals and bearings.
- How Often to Lubricate Different Components –
- Bearings: Most dredge pumps require bearing lubrication every 8 to 12 hours of operation.
- Seals: Inspect and lubricate seals weekly or more frequently for high-demand operations.
- Impeller Shaft: Lubricate the shaft according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, typically every 24 to 48 hours of use.
Due to the abrasive nature of gold mining slurry, a gold dredge pump may require additional lubrication. In contrast, a suction dredge pump may require more frequent lubrication of seals and bearings to maintain strong suction and prevent cavitation.
Monitoring Performance Indicators
Monitoring the performance of your dredge pump during operation helps detect early signs of wear or malfunction, allowing for timely corrective action. Ignoring these indicators can lead to reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, and eventual pump failure.
- Signs of Cavitation and Reduced Suction Power – Cavitation occurs when vapor bubbles form in the pump due to low pressure, causing vibration and impeller damage. If you notice reduced suction power, inspect the suction line for blockages and check for leaks that could introduce air into the system.
- Fluctuations in Pressure and Flow Rates – Sudden changes in discharge pressure or flow rate can indicate a blockage, misaligned impeller, or damaged casing. Monitor pressure gauges closely and address any irregularities immediately.
- Unusual Noise or Vibration and How to Address Them – Misalignment, worn bearings, or an imbalanced impeller often cause excessive noise or vibration. Stop the pump and inspect the impeller, bearings, and motor coupling for damage.
Regular performance monitoring is especially important for gold dredge pumps and suction dredge pumps. Gold dredge pumps often experience increased wear due to abrasive gold-bearing sediment. In contrast, suction dredge pumps rely on consistent suction power, making them more susceptible to cavitation and pressure loss.
Preventative Maintenance Strategies
Preventative maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your dredge pump. By proactively addressing wear and potential issues before they become serious problems, you can avoid costly repairs, reduce downtime, and maintain consistent operational performance. A well-planned maintenance strategy ensures that your dredge pump remains in peak working condition, whether you’re operating a gold dredge pump or a suction dredge pump.
Establishing a Maintenance Schedule
Setting up a structured maintenance schedule is one of the most effective ways to prevent breakdowns and extend the life of your dredge pump. Consistency is key — following a detailed monthly and annual plan helps identify and address issues before they escalate.
- How to Set Up a Monthly and Annual Maintenance Plan
- Monthly Maintenance:
- Inspect impellers and casings for signs of wear.
- Check seals and bearings for leaks or damage.
- Ensure proper alignment of the motor and pump.
- Test the suction and discharge pressure to confirm optimal performance.
- Annual Maintenance:
- Fully disassemble the pump for a detailed inspection.
- Replace worn components such as impellers, seals, and bearings.
- Check for internal corrosion or damage to the pump casing.
- Recoat or reline internal surfaces if necessary to improve wear resistance.
- Monthly Maintenance:
- Keeping Detailed Maintenance Records for Tracking Performance
- Maintain a log of all maintenance activities, including inspections, repairs, and replacements.
- Record performance indicators like suction power, discharge pressure, and motor temperature to identify trends over time.
- Tracking maintenance history allows you to anticipate when key components will need replacement and adjust the schedule accordingly.
Due to the abrasive nature of the gold-bearing slurry, monthly inspections of impeller wear and suction efficiency are particularly important for high-performance pumps like gold dredge pumps. Suction dredge pumps require consistent pressure testing and suction line inspections to prevent cavitation and pressure loss.
Replacing Wear Components
All dredge pumps experience wear over time, particularly when handling abrasive materials or operating under high pressure. Knowing when to replace key components is critical for maintaining efficiency and preventing unplanned downtime.
- When to Replace Impellers, Seals, and Bearings
- Impellers: Replace impellers when you notice signs of excessive wear, such as reduced suction power or vibration. Worn impellers can cause cavitation and loss of efficiency.
- Seals: Leaking or damaged seals should be replaced immediately to prevent fluid loss and pressure drops.
- Bearings: Bearings should be replaced if you notice increased noise, vibration, or overheating during operation.
- Using OEM Parts Versus Aftermarket Parts
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Parts are designed specifically for your dredge pump, ensuring a precise fit and optimal performance.
- Aftermarket Parts: These may be cheaper but can compromise pump efficiency and lifespan if they don’t match the manufacturer’s specifications.
- For critical equipment like gold dredge pumps and suction dredge pumps, OEM parts are usually the best choice to ensure reliable operation under demanding conditions.
Due to the abrasive nature of gold-mining materials, impellers and seals in gold dredge pumps may need to be replaced more frequently. Suction dredge pumps require periodic replacement of suction lines and impellers to maintain strong vacuum pressure.
Protecting Against Corrosion and Abrasion
Corrosion and abrasion are two of the most common causes of dredge pump failure. Protecting the pump’s internal components from abrasive wear and chemical damage helps extend its lifespan and maintain performance.
- Coating Options to Reduce Wear
- Epoxy-based coatings are highly effective at protecting the internal surfaces of dredge pumps from abrasive materials and corrosion.
- Rubber linings can absorb impact and reduce wear on impellers and casings.
- Ceramic coatings provide excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and abrasive slurry.
- Using Protective Linings and Materials
- Polyurethane linings are ideal for protecting suction and discharge lines from abrasive sediment.
- Stainless steel and hardened alloys can be used for impellers and casings to increase resistance to wear and corrosion.
- For gold dredge pumps, wear-resistant materials like chromium and nickel alloys are recommended to handle abrasive gold slurry.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with regular maintenance, dredge pumps can encounter operational issues that reduce efficiency and increase wear. Identifying and addressing these problems early is essential for maintaining peak performance and preventing costly downtime. Whether you’re operating a gold dredge pump in mining operations or a suction dredge pump for underwater excavation, understanding how to troubleshoot common issues will keep your equipment running smoothly.
Loss of Suction Power
Dredge pump operators commonly experience a drop in suction power. Reduced suction efficiency can quickly impact the overall productivity of a dredging operation.
Causes and How to Fix Them:
- Blocked Intake or Discharge
- Sediment, debris, and large particles can accumulate in the intake or discharge lines, restricting flow and reducing suction power.
- Solution: Stop the pump and inspect the intake and discharge lines for blockages. Remove any debris and flush the system to clear any obstructions.
- Worn Impellers or Casings
- The impeller creates the suction and discharge force, while the casing directs the flow of material. Over time, abrasive materials can wear down both components, reducing their efficiency.
- Solution: Inspect the impeller and casing regularly for signs of wear. Replace worn parts with OEM components to restore suction power.
- Air Leaks in the Suction Line
- Even a small air leak in the suction line can disrupt pressure and cause cavitation, reducing suction capacity.
- Solution: Inspect the suction line and all fittings for leaks. Tighten loose connections and replace damaged seals to restore vacuum pressure.
For gold dredge pumps, suction issues are often caused by highly abrasive slurry wearing down the impeller and suction line. In suction dredge pumps, loss of suction is commonly linked to air leaks or intake blockages, making regular inspection of the suction line essential.
Overheating
An overheating dredge pump can prematurely fail seals, bearings, and other critical components. Mechanical or operational issues that restrict proper cooling or create excessive friction often cause overheating.
Causes of Overheating:
- Improper Lubrication
- Bearings and seals rely on proper lubrication to reduce friction and dissipate heat. Insufficient or incorrect lubrication can cause excessive heat buildup.
- Solution: Lubricate the pump according to the manufacturer’s specifications. Use the correct type and amount of lubricant for its operating conditions.
- Blockages
- Blocked intake or discharge lines force the pump to work harder, increasing internal pressure and generating excess heat.
- Solution: Clear all blockages and flush the system to restore normal flow.
- Pump Misalignment
- Misalignment between the pump and motor increases mechanical strain, causing overheating in the bearings and shaft.
- Solution: Use an alignment tool to adjust the motor and pump connection properly. Recheck alignment after any major repairs or relocations.
Overheating is particularly common in gold dredge pumps due to the abrasive nature of the gold-mining slurry, which increases internal friction. Suction dredge pumps can overheat if the suction line is partially blocked, forcing the pump to work harder.
Vibration and Noise
Unusual vibration and noise are early warning signs of mechanical issues in a dredge pump. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to more severe damage and costly repairs.
Diagnosing Vibration Issues:
- Misaligned Shafts
- If the pump shaft and motor are not properly aligned, uneven stress on the bearings and impeller results in excessive vibration.
- Solution: Check shaft alignment with a laser or dial indicator. Adjust as needed to restore proper alignment.
- Damaged Impellers
- A bent or cracked impeller creates an imbalance that generates vibration and noise.
- Solution: Inspect the impeller for damage. Replace it with an OEM part if necessary.
- Loose Fittings
- Vibration can loosen bolts and fittings, causing rattling and excessive movement during operation.
- Solution: Tighten all bolts and fittings. Use thread-locking compounds to prevent future loosening.
For gold dredge pumps, vibration issues often stem from the abrasive nature of the gold slurry, which can damage impellers and shafts. In suction dredge pumps, vibration is typically caused by misalignment or debris in the suction line.
Extending the Lifespan of Your Dredge Pump

Maximizing the lifespan of your dredge pump is essential for maintaining operational efficiency and reducing long-term costs. A well-maintained dredge pump delivers consistent performance, reduces downtime, and minimizes the need for expensive repairs or replacements. Whether you’re operating a gold dredge pump for mining or a suction dredge pump for underwater excavation, following best practices for storage, performance testing, and component upgrades can significantly extend the life of your equipment.
Proper Storage and Handling
How you store and handle your dredge pump when it’s not in use plays a crucial role in its longevity. Exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures, and improper handling can lead to premature wear and component failure.
- Draining and Cleaning the Pump After Each Use
- After each dredging operation, the pump must be thoroughly drained and cleaned to remove sediment, debris, and corrosive materials.
- Any leftover slurry or moisture can cause internal corrosion, especially in components like impellers and casings.
- Removing abrasive gold slurry reduces wear on internal components in gold dredge pumps. Suction dredge pumps require extra attention to their suction lines and discharge hoses to prevent sediment buildup.
- Storing in a Dry, Temperature-Controlled Environment
- Store the pump in a dry location with stable temperatures to prevent condensation and corrosion.
- Avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures, which can cause seals and hoses to degrade over time.
- If the dredge pump must be stored outdoors, cover it with a protective tarp and elevate it off the ground to prevent moisture buildup.
Proper storage is especially important for gold dredge pumps operating in mining environments, where abrasive materials can accelerate internal wear. Suction dredge pumps used in marine environments are prone to saltwater corrosion, making dry and protected storage essential.
Regular Performance Testing
Conducting regular performance tests helps ensure that your dredge pump is operating at optimal efficiency. Monitoring flow rates, pressure levels, and other key performance indicators allow you to identify early signs of wear and make adjustments before problems arise.
- Conducting Flow Rate and Pressure Tests
- Measure the flow rate and discharge pressure under normal operating conditions.
- Compare test results with manufacturer specifications to detect performance drops.
- For suction dredge pumps, reduced suction pressure may indicate air leaks or blockages in the suction line.
- For gold dredge pumps, a drop in discharge pressure may signal worn impellers or casing damage due to abrasive slurry.
- Adjusting Performance Based on Testing Data
- If flow rates and pressure levels are below the expected range, adjust pump settings or inspect for damaged components.
- Rebalance impellers, clean suction lines, and check for misalignment or blockages.
- Monitor electrical consumption for electric dredge pumps — increased power usage may indicate mechanical strain or internal resistance.
Consistent testing allows you to make informed decisions about when to replace parts or upgrade components, ensuring that your dredge pump continues to operate efficiently.
Upgrading Components
Upgrading key components can significantly improve the durability and performance of your dredge pump. Replacing worn or outdated parts with higher-quality materials helps the pump withstand harsh operating conditions and extend its lifespan.
- Installing Higher-Wear-Resistant Impellers and Casings
- Standard impellers and casings may degrade quickly when handling abrasive materials.
- Upgrade to impellers made from high-chrome alloys, hardened steel, or ceramic-coated materials to increase resistance to wear.
- For gold dredge pumps, high-chrome impellers and rubber-lined casings are ideal for handling abrasive gold-bearing slurry.
- For suction dredge pumps, wear-resistant coatings and reinforced impellers help maintain strong suction power.
- Upgrading Motor Efficiency and Control Systems
- Older motors are often less efficient and more prone to overheating.
- Installing high-efficiency motors reduces energy consumption and improves overall pump performance.
- Adding a variable frequency drive (VFD) allows you to adjust pump speed based on operational demands, reducing strain on the motor and impellers.
Upgrading to advanced materials and more efficient components extends the pump’s lifespan, improves performance, and reduces operating costs.
Specific Considerations for Gold Dredge Pumps and Suction Dredge Pumps
Different types of dredge pumps have unique operational challenges and maintenance requirements. Gold dredge pumps are designed to handle abrasive materials commonly found in mining operations, while suction dredge pumps rely on consistent vacuum pressure to lift sediment and slurry. Understanding the specific needs of these pumps helps ensure consistent performance and reduces the risk of breakdowns.
Gold Dredge Pump Maintenance
Due to the nature of gold mining materials, gold dredge pumps are subjected to extreme wear and abrasion. Gold-bearing slurry typically contains a high concentration of sand, gravel, and fine particles, which can rapidly wear down pump components if not properly managed.
- Managing Abrasive Material Handling
- The high abrasiveness of gold-bearing material increases stress on the impeller, casing, and seals.
- To prevent rapid wear, gold dredge pumps should be operated at the correct speed and pressure to reduce excessive material impact.
- Use a slower impeller speed when handling highly abrasive material to reduce internal friction and minimize wear.
- Install intake screens to filter out large debris and reduce the load on the impeller.
- Importance of Using Wear-Resistant Materials
- Standard pump materials are often inadequate for handling gold mining slurry due to its abrasive nature.
- Impellers and casings made from high-chrome alloys or hardened steel offer greater resistance to wear.
- Rubber linings or ceramic coatings can help protect the internal surfaces of the pump from abrasive damage.
- High-quality seals and bearings should be used to withstand constant exposure to abrasive slurry.
Regular inspection and replacement of worn components are crucial for maintaining the performance of a gold dredge pump. Upgrading to more wear-resistant materials helps extend the pump’s lifespan and reduces long-term maintenance costs.
Suction Dredge Pump Maintenance
Suction dredge pumps rely on strong and consistent vacuum pressure to lift sediment and slurry from the waterbed. Any disruption in the suction line or loss of pressure can reduce efficiency and lead to operational downtime.
- Checking Suction Line Integrity
- Air leaks in the suction line are one of the most common causes of reduced suction power in suction dredge pumps.
- Regularly inspect the entire length of the suction line for cracks, holes, or loose connections.
- Ensure that all hose clamps and fittings are tightened and that the suction line is properly sealed.
- Look for signs of internal wear in the suction line. Abrasive materials can gradually erode the inner surface.
- Ensuring Proper Priming Before Operation
- Suction dredge pumps require proper priming to establish the vacuum necessary for material transport.
- If the pump is not properly primed, it will draw in air instead of slurry, reducing suction capacity and increasing the risk of cavitation.
- Follow the manufacturer’s priming procedure carefully to ensure the pump is filled with liquid and all air is removed from the suction line.
- Install a foot valve at the end of the suction line to help maintain prime and prevent backflow.
For suction dredge pumps used in marine or river dredging, regular inspection and maintenance of the suction line are critical to maintaining consistent performance. Ensuring proper priming before each use helps maximize efficiency and reduce wear on the impeller and seals.
Conclusion
Proper maintenance and care are essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficiency of your dredge pump. By following a structured maintenance schedule, monitoring performance indicators, and upgrading to wear-resistant components, you can prevent costly breakdowns and ensure consistent performance. Whether you’re operating a gold dredge pump to handle abrasive gold-bearing slurry or a suction dredge pump for underwater excavation, understanding the specific maintenance needs of each type of pump is key to long-term success. Investing in high-quality materials, conducting regular inspections, and addressing issues early will keep your dredge pump running at peak efficiency, reduce operational costs, and extend the life of your equipment.






